AV-Comparatives takes a deep dive into LSASS Security Features Against Credential Dumping for Enterprise Products
AV-Comparatives tested LSASS Protection Features for Business Security Products - MITRE ATT&CK tactics and techniques

Logo AV-Comparatives
Windows Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) is one of the cybercriminals’ targets when launching targeted attacks on an organisation’s network
Protection against LSASS credential dumping
Depending on the installed security product and applicable policy, it could be easier or harder for an attacker to get hold of Windows user credentials by dumping the address memory of LSASS.
Some security products include specific hardening measures to protect the LSASS process and prevent credential dumping.
However, it may not always be possible to use these more restrictive policies in some organizations’ environments, as they might cause problems with some legacy apps or apps that are not well programmed. Hence, IT administrators should test a product’s hardening settings to see if they have any unwanted side effects.
Blue teams should still assume that determined attackers will find a way to dump the LSASS process, even if the installed security products use specific code to harden the LSASS process against attacks. That is to say; they may still be able to extract user credentials from the LSASS process. In addition to the specific LSASS-hardening measures, security products may prevent credential dumping by, e.g., the antivirus module; this may detect the malware or other files created by the malware or use behavioural detection to block the malicious actions. In some cases, the security product may not stop the attack. Still, it will at least produce an alert, thus warning the system administrator that the malicious actions should be investigated.
Some business security products have their LSASS hardening measures activated by default. Examples are Avast Ultimate Business Security, Bitdefender GravityZone Business Security Enterprise, and Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert. Microsoft also provides two features specifically used to protect the LSASS process: PPL (Protected Process Light) and ASR (attack surface reduction) rules. PPL is enabled by default on Windows 11 but currently not on Windows 10; it is included in the Professional, Enterprise and Education variants of Windows 10/11. The ASR rules can be used in organisations’ networks in conjunction with Microsoft Defender and currently need to be proactively configured on either OS.
Test of credential-dumping protection in security products
Given the importance of preventing LSASS credential dumping, in May 2022, AV-Comparatives tried out some business security products to determine how well their hardening measures protected against attacks on LSASS.
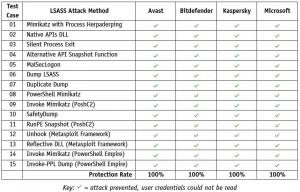
Below AV-C lists some products (made by Avast, Bitdefender, Kaspersky and Microsoft) that showed effective protection against the 15 attacks used in our test, with their respective LSASS hardening measures enabled.
The table above includes results for the following products (with LSASS protection settings enabled): Avast Ultimate Business Security, Bitdefender GravityZone Business Security Enterprise, Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Microsoft asked us to publish the results of an additional test of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint that we ran without their LSASS protection features (PPL and ASR) enabled. This was done to determine if the attacks listed above would be detected by other Microsoft security features. For each test case, we checked to see if the attack was correctly attributed to the MITRE ATT&CK tactics and techniques about LSASS in the case of detections or active alerts by the security product. When the security product prevented the attack, we checked to see which information about the threat was provided in the admin console. This test's methodology and other details can be found in this PDF. For additional information, please also read this blog entry from Microsoft.
Peter Stelzhammer
AV-Comparatives
+ +43720115542
media@av-comparatives.org
Visit us on social media:
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.

