ERCOT 2023 Mid-Year Electric Grid RECAP
he summer of 2023 in Texas brought sweltering temperatures and unprecedented energy demands to the ERCOT grid.
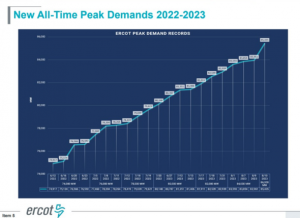
HOUSTON, TEXAS, UNITED STATES, November 24, 2023 /EINPresswire.com/ -- The summer of 2023 in Texas brought sweltering temperatures and unprecedented energy demands to the ERCOT grid. With Austin experiencing 105+ degree temperatures for a remarkable 42 days, breaking the previous record of 26 days set in 2011, and a peak load demand exceeding 80 gigawatts (GW) for 49 days, surpassing the all-time high set in July 2022, it was a season of records. This recap highlights key takeaways from this scorching summer.New All-Time Peak Load Demand
The surge in peak load demand in 2023 can be attributed to economic load growth, particularly in the industrial sector, coupled with soaring temperatures. Compared to the prior year, the summer of 2023 was drier and hotter, resulting in a significant increase in peak load demand over the past two years.
Shifting Scarcity Period
ERCOT has been steadily incorporating renewable energy sources, with solar and wind now accounting for approximately 40% of the grid's generation. Notably, solar generation has substantially increased since 2022. This transition in the energy mix caused the scarcity period, the time when the grid faces its tightest supply-demand balance, to occur later in the day. In previous years, peak load demand typically occurred around 3:00 pm to 4:00 pm when temperatures were at their peak. In 2023, the scarcity period shifted to 7:00 pm or 8:00 pm, coinciding with the solar ramp-down period. Thankfully, the increased number of solar resources proved capable of meeting afternoon peak demand, but challenges arose when the grid lost its solar energy during evening hours.
Conservation Notices
Wind generation played a pivotal role in meeting evening demand, but low wind output became a significant factor on days when conservation notices were issued. These notices were used to lower consumption and proved effective during periods of low wind generation. ERCOT issued 11 conservation calls between June and September. On days when wind generation fell short of forecasts, all available generation and ancillary services were fully utilized to meet demand, with batteries helping to fill supply gaps.
Energy Emergency Alert
The summer of 2023 witnessed several new all-time peak demand records, with the highest demand reaching 85.4 GW on August 10th, a 5.4 GW increase from June. On September 6th, the grid faced its tightest day of the summer, leading to an Energy Emergency Alert (EEA) Level 2. EEA Level 2 is declared when operating reserves fall below 1,750 MW and are not expected to recover within 30 minutes, while Level 3 is the most severe and can result in controlled outages. South Texas transmission constraints and thermal generation plant outages triggered the EEA Level 2 alert. Additionally, higher temperatures, increased demand, and resource limitations in North and West Texas contributed to transmission constraints in Central Texas, necessitating the EEA protocols.
Higher Energy and Ancillary Prices
Comparatively, energy and ancillary service costs were higher in the summer of 2023 than in the previous two summers. This increase was primarily due to the greater reliance on ancillary services needed to manage real-time operational risks in the current market conditions. As intermittent resources play a larger role in the grid, the need for additional ancillary services to mitigate the risk of missing forecasts remains.
Looking Ahead to Winter 2023-2024
The grid's volatility, driven by factors such as extreme weather, load growth, and the early retirement of dispatchable power plants, will continue to pose challenges during the winter months. While ERCOT does not anticipate emergency conditions this winter, they acknowledge an elevated risk probability. To mitigate this risk, ERCOT plans to procure 3,000 MW of capacity, considering the significant peak load growth since the previous winter and the extreme winter weather events of the past two years. This additional capacity aims to ensure adequate load and operating reserve coverage during winter weather events.
In Conclusion
Managing a growing demand and a dynamic load environment in Texas is more challenging than ever for grid operators. While the focus has primarily been on the supply side of the equation, ERCOT is also examining transmission and demand-side solutions to alleviate congestion constraints and reduce load demand. A holistic approach is necessary to meet load requirements and maintain a comfortable operating reserve margin as Texas continues to navigate the evolving energy landscape.
Enrique Ortegon
Enrique Ortegon
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.