Innovation Week 2023 - Indirect electrification and workshops: As it Happens
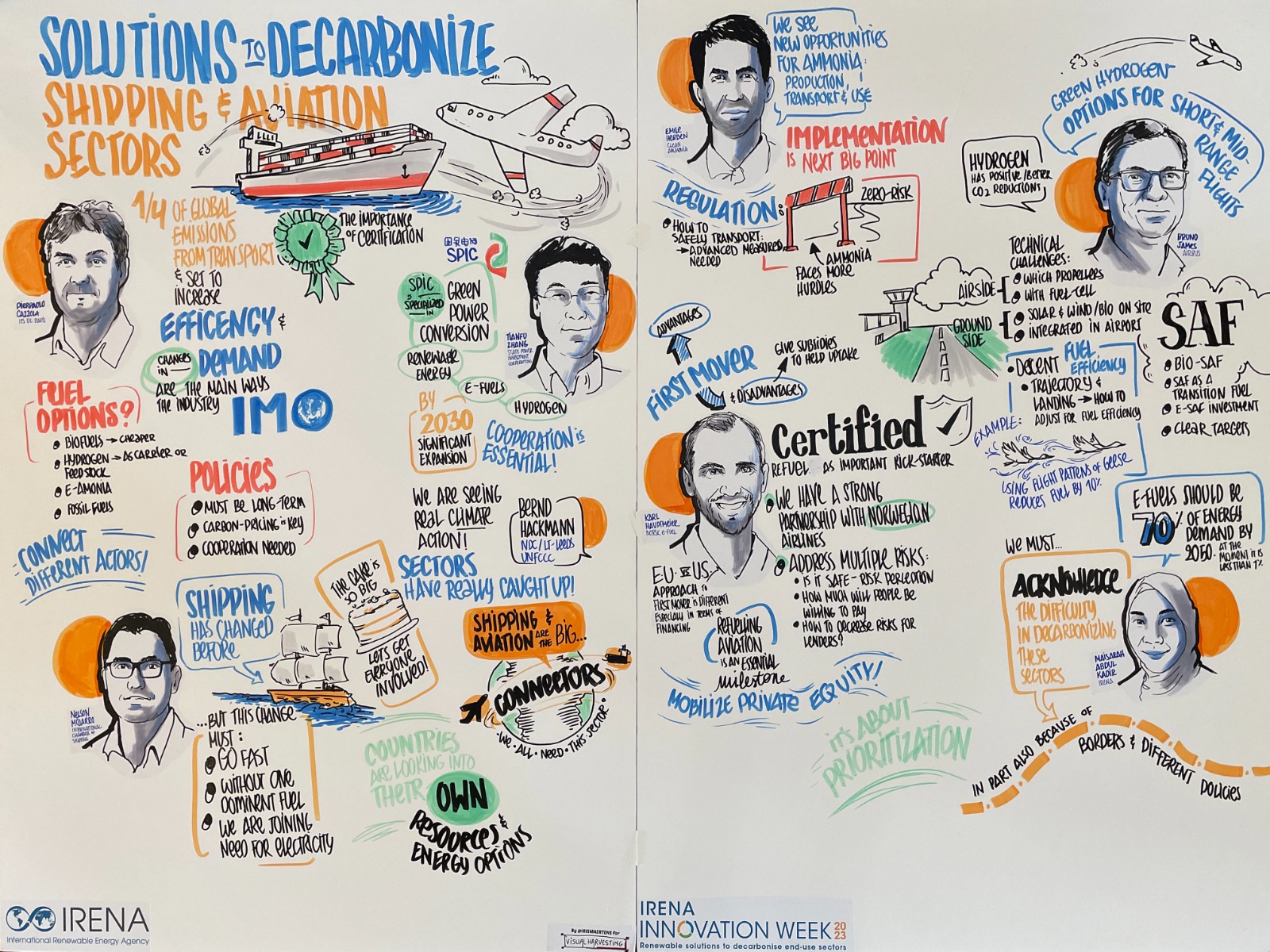
Solutions to decarbonise the shipping and aviation sectors
Decarbonisation of the shipping and aviation sectors remains a challenge on the path to 1.5°C. In this session, the panelists will discuss potential innovative solutions for these hard to abate sectors.
Kicking of the discussion with a keynote, Pierpaolo Cazzola, Director of the European Transport and Energy Research Center, ITS UC Davis outlined areas that need attention in the shipping and aviation sector. He mentioned that the technical solutions offer efficiency and operational improvements but readiness, scale-up and cost are the key considerations. For example, electrification is a viable solution for short haul aviation only, while renewable e-fuels such as e-ammonia and e-ethanol are competitive candidates for maritime fuels although their adoption remains uncertain. Finally, policy support for innovation and tech development is crucial.
Renewables play a key role in the decarbonisation of the industry. Carlos Ruiz, Programme Officer – Innovation and End-use Sectors, IRENA, stated that not all solutions are suitable for the shipping and aviation sectors and a smart approach to prioritization of available options, planning, timely development of the infrastructure and regulations are vital.
International shipping is a key sector of the economy with as much as 90% of worldwide trade transacted via ocean going vessels. IRENA report, Pathway to Decarbonise the Shipping Sector by 2050 explores the options and actions needed to progress towards a decarbonised maritime shipping sector by 2050 identifying a realistic pathway to reach the 1.5°C climate goal.
The summary of the key points from this session is provided in the visualisation below.
Future materials for EV batteries
IRENA research shows that the number of electric passenger cars would grow to 360 million by 2023, and 2 180 million by 2050 under IRENA's 1.5°C Scenario. The demand for EVs will drive the need for materials such as lithium, graphite and cobalt. It is therefore imperative to develop sustainable and equitable supply chains for critical materials.
The panellists outlined key innovations that promote the development of sustainable supply chains. These, among others, include adapting battery manufacturing processes that are less reliant on the associated battery chemistries; developing circular economy initiatives that allow for all EV battery stakeholders to recycle of critical materials effectively; enhancing R&D capabilities to allow for new technologies to be integrated into the market; and developing standardization protocols for the manufacturing process.
Read the article on why EV-battery innovation is key to sparking a renewable revolution.
Grid Evolution: Transforming Energy Landscapes in Developing Countries and SIDS
This session focused on innovations in technology, financial mechanisms, technical standards, best practices, and strategic approaches to modernize electricity grids and increase their reliability while integrating variable renewables in developing countries and SIDS systems.
In his keynote, Simon Benmarraze, Team lead, Technology and Infrastructure, IRENA, set the scene statiung that the solution lies in developing a climate adaptation strategy, both in transmission and distribution systems, and developing resilient enhancement measures for short- and long-term solutions.
“A critical point for a successful transition is stakeholder collaboration from all actors including utilities, regulators, private sector, as well as financial institutions,” said H.E Mr Kaleb Udui, Jr., Minister of Finance, Palau. Only balance energy efficiency and renewable energy deployment we can reach 100% renewable target, he continued.
The key points raised centred around the grid modernization helps support end-use electrification and improve power system resilience. Smooth collaboration between utilities, regulators, and other stakeholders is required to ensure that grid modernization and end-use electrification are effectively integrated. Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change and there has been a growing focus on improving the efficiency and reliability of power grids, as well as integrating renewable energy power into the grid. Modernizing the grid can allow for better management of distributed energy resources, including rooftop solar panels and EVs.
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
