Hot Swap Controllers: Safely Inserting and Removing Devices from Live Systems
Hot swap controllers are integrated circuits that allow a device to be inserted or removed from a live system without causing damage or disruption.
SHENZHEN, GUANGDONG, CHINA, March 2, 2023 /EINPresswire.com/ --
Hot swap controllers are integrated circuits that allow a device to be inserted or removed from a live system without causing damage or disruption. They are commonly used in applications where a line card or a module needs to be plugged into a backplane that has power applied.
Hot swap controllers perform several functions to ensure safe and reliable operation of the system. They limit the inrush current when a device is first inserted, preventing voltage drops and glitches on the power supply rails. They also protect against short circuits, overvoltage, overcurrent, overtemperature, reverse polarity, and other fault conditions that may occur while the device is in operation. They monitor and report various parameters such as voltage, current, power, temperature, and status using analog or digital interfaces.
Hot swap controllers can be classified into different types based on their operating voltage range, architecture, features, and performance. Some examples are:
1. Low voltage hot swap controllers: These operate from 0 V to 20 V and are suitable for systems that use standard logic levels such as 3.3 V, 5 V, or 12 V. They typically use MOSFETs as power switches and have simple control schemes.
2. High voltage hot swap controllers: These operate from 20 V to 1000 V and are suitable for systems that use high voltage rails such as -48 V or +48 V. They typically use IGBTs or FETs as power switches and have more complex control schemes that involve galvanic isolation, soft start, current sensing, fault detection, etc.
3. eFuses: These are single-chip solutions that integrate a power switch with protection features such as overvoltage clamping, current limiting, thermal shutdown, etc. They offer fast response time and small footprint compared to discrete solutions.
4. Hot-swap controllers are widely used in various industries such as telecommunications (e.g., AdvancedTCA), datacom (e.g., servers), industrial (e.g., PLCs), automotive (e.g., battery management), medical (e.g., MRI scanners), etc.
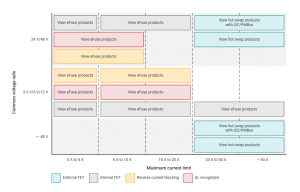
Here are some products from different manufacturers that offer various features and specifications:
Analog Devices: They offer a wide range of hot swap controllers for low voltage, high voltage, high current, and high power applications. Some examples are:
ADM1270: A high voltage input protection device that provides overvoltage protection up to 140 V with an integrated 12 V to 80 V MOSFET driver.
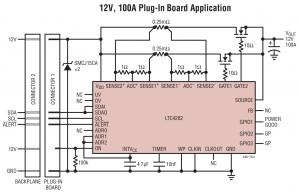
LTC4282: A negative voltage hot swap controller that supports -20 V to -100 V operation with a bidirectional power monitor and an I2C interface.
LTC4233: A dual channel hot swap controller that supports 2.9 V to 29 V operation with independent current limit, fault timer, and power good signals for each channel.
Figure 1. shows a typical application circuit for a high-voltage hot swap controller using LTC4282.
Texas Instruments: They offer a variety of eFuses and hot swap controllers for low voltage, medium voltage, and high voltage applications. Some examples are:
TPS25982: A USB Type-C port protector that provides overvoltage protection up to 28 V with an integrated FET switch and a CC pin multiplexer.
TPS24752: A medium voltage hot swap controller that supports 4.5 V to 18 V operation with adjustable current limit, soft start, fault timer, and power good signal.
UCC27714: A high side gate driver that enables high voltage hot swap control using external FETs for up to 600 V operation.
Figure 2. shows a typical application circuit for a low-voltage eFuse using TPS25982.
Microchip Technology: They offer a range of hot swap controllers for low voltage and medium voltage applications. Some examples are:
MIC2582: A single channel hot swap controller that supports up to 16.5 V operation with inrush current limiting, output voltage slew rate control, overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, etc.
MIC2588: A dual channel hot swap controller that supports up to 16.5 V operation with independent control logic for each channel and shared fault reporting via an open-drain output pin.
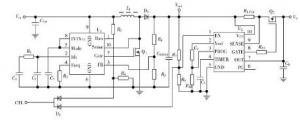
MIC2590B: A medium voltage hot swap controller that supports up to 80 V operation with programmable current limit, soft start time, fault timer delay time.
Figure 3. shows a typical application circuit for a medium-voltage hot swap controller using MIC2590B.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hot swap controllers are crucial integrated circuits used to ensure the safe and reliable operation of electronic systems when a device is inserted or removed from a live system. They offer several functions such as limiting inrush current, protecting against various fault conditions, and monitoring and reporting different parameters. Hot swap controllers can be classified into different types based on their operating voltage range, architecture, features, and performance. They are widely used in various industries such as telecommunications, datacom, industrial, automotive, medical, etc. Different manufacturers such as Analog Devices, Texas Instruments, and Microchip Technology offer a range of hot swap controllers with various features and specifications to cater to different applications.
Click Here to get more details about Hot swap controllers.
Gloria
Utmel Electronic Limited
+86 137 2898 8459
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.